At My Design Minds, we provide custom pressure die casting parts tailored for various industries, including automotive, aerospace, and electronics. It is most widely known for its ability to produce complex, high-performance parts with good quality surface finish and close dimensional tolerances. It is the pillar of contemporary manufacture, especially in the automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer products sectors. This paper discusses principles, process, types, benefits, drawbacks, applications, and developments in pressure die casting.

Principles of Pressure Die Casting
Unlike gravity casting, the pressure die casting process step by step involves rapid metal injection and solidification to ensure quality and dimensional precision. This is a matter of quick and full filling of the mould even for thin-sectioned and complex parts.
Major Steps involved in Pressure Die Casting Process
Here is the pressure die casting process step by step as followed by our expert team at My Design Minds.
1.Die preparation
The die is usually constructed of hardened tool steel, washed, and subsequently lubricated for the purpose of furnishing a smooth movement of metal as well as part ejection.
2. Melting of the metal:
Metal or alloy to be used (usually aluminium, zinc, or magnesium) is melted in the furnace to the casting temperature.
3. Injection:
Hot metal is struck at high pressure (1,500 to over 25,000 psi) into the die cavity by a piston or plunger.
4. Solidification:
Metal quickly freezes and solidifies in the die, in the form of the cavity itself.
5. Ejection:
Freezing after which the die is opened and ejector pins force the casting out of the mould.
6. Trimming and Finishing:
Excess material is cut from flash, runners, and gates, and the casting may be subjected to further finishing such as machining, coating, or heat treatment.
Types of Pressure Die Casting
1. Hot Chamber Die Casting
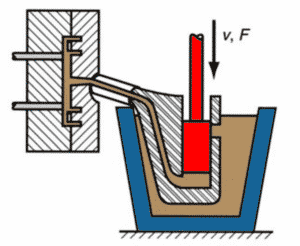
Process: Injection system is dipped in molten metal.
Meets that can be used: Low-melting-point alloys such as zinc, magnesium, and lead.
Advantages: Quick cycle times, less metal oxidation, and cost-effective for small- to medium-sized parts.
2. Cold Chamber Die Casting
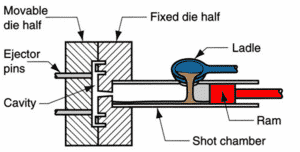
Process: Injection of hot metal into a cold chamber prior to injection into the die.
Fit Metals: Brass, copper, and high-melting aluminium alloys.
Advantages: To be used only with metals which would spoil the injection system in hot chamber equipment; best to cast large sizes.
Both methods play key roles in different applications. Hot chamber vs cold chamber die casting is often chosen based on the alloy and production speed.
Pressure Die Casting Advantages
Production Volumes: Long cycle intervals to produce thousands of identical components quickly with little labour.
Low Surface Finish: No post-machining or minimal post-machining is necessary.
Dimension Accuracy: ±0.1 mm tolerance can be achieved, with a minimal amount of machining.
Narrow Shapes: Delicate sections, fine detail, and intricate shapes are easily cast.
Material Economy: Low wastage because there is accurate control and possibility of reusing scrap material.
Strength and Toughness: Fast rates of solidification and fine microstructure improve mechanical properties.
The advantages and disadvantages of pressure die casting make it ideal for high-volume production where dimensional accuracy and repeatability are critical.
Pressure Die Casting Limitations
High Initial Cost: Die making and tooling are costly, so the process is economical only for mass production.
Limited Choice of Alloys: All metals are not being used; ferrous metals such as steel and iron can’t be used because of die wear.
Porosity: To reduce porosity, many manufacturers adopt the low-porosity pressure die casting process using vacuum systems.
Size Limitations of Parts: Normally appropriate for parts not bigger than medium size.
Complexity of the Die: The dies need to be properly designed in a way that they allow proper metal flow, cooling, and ejection.
Applications of Pressure Die Casting
Pressure die casting is only necessary in high-quantity, high-precision metal part applications:
Automotive: We specialize in high pressure die casting for automotive components such as engine parts and structural brackets.
Aerospace: Structural parts, housings, and brackets.
Consumer Electronics: Laptop, smartphone, and camera cases.
Home Appliances: Washer parts, refrigerator parts, and small appliance parts.
Industrial Machines: Pump housing, valves, and fittings.
Recent Developments
Die casting also changes with new technology to enhance quality, efficiency, and sustainability even more:
Vacuum Die Casting: Reduces porosity by evacuation of air from the die cavity prior to injection.
Sophisticated Simulation Software: Allows virtual simulation of metal flow, cooling, and solidification, minimizing defects and die design optimization.
Automated Systems: Robotic and automation offers improved consistency, safety, and productivity.
New Alloys: Advanced high-performance alloys with improved strength and corrosion resistance
Environmental Initiatives: Increased recycling of scrap metal and more energy-efficient melting processes.
Conclusion
Pressure die casting is a dangerous manufacturing process that allows for speed, accuracy, and flexibility. Its potential to produce high-class complex parts in large quantities makes it the most appropriate process in most industries. Notwithstanding its high cost and expertise, continued technological advancements further enhance its scope and variety, making it viable in modern manufacturing years to come.
As one of the leading aluminum pressure die casting manufacturers and service providers, My Design Minds offers precision die casting services near me for clients across Delhi NCR and globally. Our pressure die casting services in India cater to diverse industries with affordable solutions and fast turnaround.
